Learning how to change router IP address might seem complex, but with clear instructions, it becomes an easy task. Changing this setting is beneficial for enhancing network security, resolving device conflicts, and optimizing network management. Most routers use well-known default IP addresses, which attackers can easily target. Adjusting your router’s IP address adds a protective barrier against unauthorized access and simplifies device connectivity. This comprehensive tutorial walks you through every step required to safely change your router’s IP. Whether you're experiencing network conflicts, improving security, or simply optimizing your network settings, this guide provides detailed, actionable instructions to ensure your home network remains secure, efficient, and trouble-free.
Why Change Your Router’s IP Address?
Changing your router’s IP address serves several important purposes. First and foremost, enhancing network security is a primary reason. Default IP addresses used by many routers are publicly known, making networks vulnerable to cyber-attacks. Assigning a unique IP reduces exposure to unauthorized access attempts, significantly bolstering your security defenses. Additionally, IP address conflicts within home or office networks can lead to frustrating connectivity issues, including devices intermittently losing internet access. Adjusting your router’s IP resolves such conflicts, allowing smooth, uninterrupted network communication. Furthermore, customizing your IP address can bypass certain limitations or geographic restrictions imposed by your Internet Service Provider (ISP). Ultimately, managing your router’s IP address not only improves security and stability but also provides greater control over your home network, ensuring optimal device performance and streamlined internet connectivity.
How to Change Your Router’s IP Address
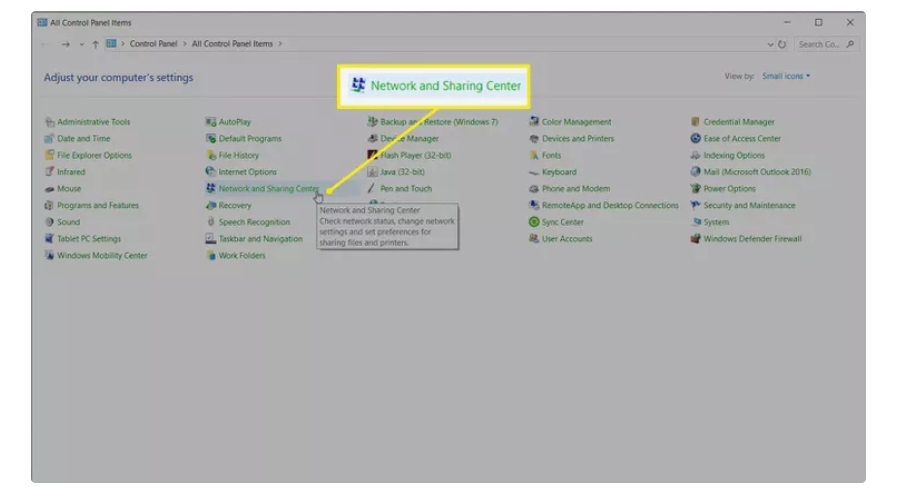
Step 1: Access Your Router’s Admin Panel
To start the process, access your router’s administration panel. First, ensure your computer or mobile device is connected directly to the router via Ethernet cable or Wi-Fi. Next, open a web browser, type your router’s default IP address (commonly 192.168.1.1 or 192.168.0.1) into the address bar, and press Enter. You should see a login page requiring your router’s username and password. Typically, these credentials are found on a sticker attached to your router or provided in its user manual. Common default login credentials are usually "admin" for both username and password, but these vary by manufacturer. If you've previously customized these credentials but cannot remember them, performing a factory reset will revert them to defaults—though this resets all other settings too. Once logged in, you gain access to essential router configurations, including IP address settings.
Step 2: Locate the IP Address Settings
After successfully logging into your router’s admin panel, you'll need to locate the IP address settings. Interfaces vary between manufacturers, but generally, the IP settings are found under sections labeled "Network," "LAN," "Local Network," or "TCP/IP Settings." Navigate carefully through these menus, paying close attention to labels like "Router IP Address" or "LAN IP Address." Avoid confusing these settings with the WAN or external IP, as altering those settings affects your router's external connectivity and should typically remain unchanged. When locating the correct setting, read all accompanying descriptions and instructions provided within the router’s interface to ensure accurate modifications. Taking this careful approach helps you make correct adjustments without inadvertently disrupting your internet connection. Clearly identifying the appropriate settings ensures a smooth process when you move to change your IP address.
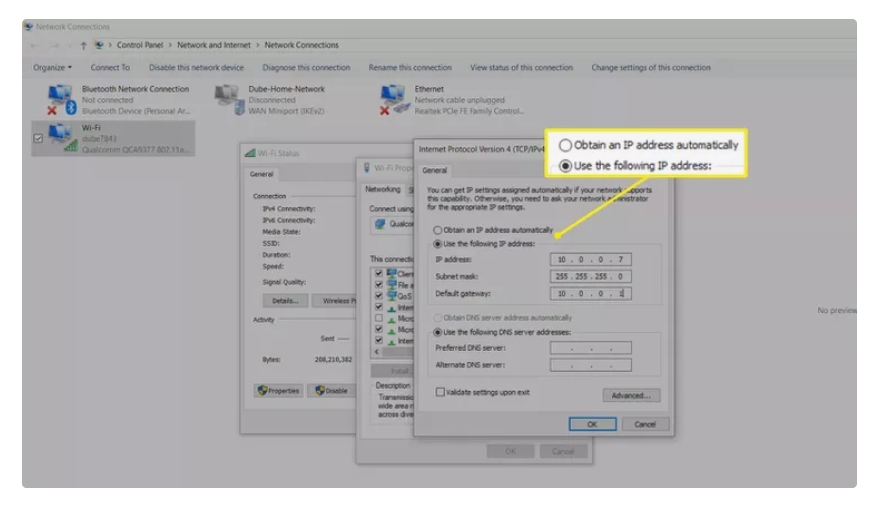
Step 3: Modify and Save the New IP Address
Now that you've identified the correct settings area, it’s time to assign your router a new IP address. Select the current IP address displayed and enter your chosen replacement address, ensuring it aligns with standard local network conventions (typically 192.168.x.x). For increased security and uniqueness, consider choosing a less common address, such as 192.168.15.1 or 192.168.20.1. Avoid commonly known addresses like 192.168.1.1, as these are easily guessed. After entering the new IP, double-check your entry for accuracy. Save your changes by clicking the appropriate button, usually labeled "Save," "Apply," or "Confirm." After saving, your router might prompt you to confirm the change once more before applying it fully. Ensure you follow any additional on-screen instructions precisely to successfully update your router’s IP address settings, ensuring your new configuration is securely implemented.
Step 4: Reboot Your Router
Once you've saved your new IP address settings, the router needs a restart to apply these updates fully. Some routers automatically reboot after changes, but others require manual rebooting. If a manual reboot is necessary, turn off your router using the power button or by unplugging its power cable from the outlet. Wait approximately 30 seconds to ensure all internal processes halt completely, then restore power by reconnecting the router. Allow a few minutes for your router to restart fully. After rebooting, reconnect your devices to the network using the updated IP configuration. Verify internet connectivity and ensure devices communicate seamlessly with each other and the router. This reboot process ensures the new IP address settings take effect completely, minimizing issues and confirming that your network now operates under the updated and secured IP configuration.
Potential Issues and Troubleshooting
IP Address Conflicts
Occasionally, after changing your router’s IP address, you may experience IP address conflicts within your network. Such conflicts arise when multiple devices attempt to use identical IP addresses, causing connectivity disruptions and instability. To resolve these issues, access your router’s administrative settings again and review the DHCP configuration. Adjust the range of IP addresses your router assigns dynamically, ensuring it excludes the router’s new IP address to prevent overlap. Additionally, configuring devices to automatically obtain IP addresses via DHCP can mitigate conflicts by allowing your router to assign unique IP addresses systematically. If conflicts persist despite DHCP adjustments, consider assigning static IP addresses individually to problematic devices. This manual allocation ensures each device holds a distinct IP, eliminating conflicts entirely, and resulting in stable, uninterrupted connectivity throughout your network.
Lost Access to Router Admin Panel
Occasionally, changing your router’s IP address can lead to temporary loss of access to its admin panel. If you experience this issue, first ensure your device is connected directly to the router and verify you're entering the newly assigned IP address accurately into your browser. Clearing your browser's cache or switching browsers may help regain access. If these steps don't work, a router reset to factory settings might become necessary. Press and hold your router’s reset button—usually located on the back panel—for roughly 10 seconds. This action resets the router to factory defaults, restoring the original IP address and login credentials. Be aware this process also deletes all customized configurations, requiring you to reconfigure settings afterward. Carefully documenting your network settings before making substantial changes helps streamline this restoration process if needed.
Conclusion
Changing your router’s IP address is an effective way to strengthen network security, reduce conflicts, and enhance overall performance. With this comprehensive tutorial on how to change router IP address, the process becomes straightforward, providing you greater control over your network. By following clearly outlined steps—accessing your router’s admin panel, locating the IP address settings, applying your new IP, and rebooting—you successfully implement important network improvements. While occasional issues like IP conflicts or access loss might occur, they’re easily resolvable through the proper troubleshooting techniques provided in this guide. Ultimately, knowing how to manage your router’s IP address ensures a more secure, efficient, and reliable home or office network, giving you the confidence and capability to handle future network adjustments with ease.
FAQ
Can changing my router’s IP address improve security?
Yes, altering your router’s default IP address enhances security by making it more difficult for unauthorized users to access your network. Default IP addresses are widely recognized targets, making personalized addresses more secure.
What should I do if I can’t access my router after changing its IP address?
If access issues occur after changing the IP address, ensure you're entering the correct new IP into your browser. Clearing the browser cache or resetting your router to factory settings can help you regain access if necessary.
Will changing the router’s IP address affect connected devices?
Changing your router’s IP address may temporarily disrupt connected devices. However, devices usually reconnect automatically under the new configuration. Brief disruptions are minimal, and long-term connectivity typically remains unaffected.