Wondering how to check browsing history on WiFi router? Monitoring internet activity can significantly enhance your home network’s security, help manage data usage, or enable better parental control. While your router holds valuable information about connected devices’ browsing patterns, accessing this data can initially seem daunting. Thankfully, checking router logs and interpreting their meaning isn't overly complicated with clear, structured guidance. In this guide, we will outline straightforward steps to locate and examine browsing history from your router effectively. Additionally, we’ll discuss alternative tools if your router lacks advanced logging features. Ready to gain clarity about your network’s activity and safeguard your home network? Let’s explore these steps together.
Can You Check the Browsing History on a WiFi Router?
Checking the browsing history on a WiFi router is typically possible; however, the available details vary depending on your router model and manufacturer. Some routers keep detailed logs showing visited URLs, device identifiers, and access times, while others record limited information such as IP addresses or device MAC addresses. Note that most routers don't specifically track detailed browsing activity from private or incognito sessions due to built-in privacy protections. To access browsing history, your router must have logging capabilities enabled. If logging isn't active by default, you may need to turn it on through your router’s administrative settings. Checking your router’s user manual or the manufacturer's website is advisable, as these resources offer guidance about your router’s particular logging capabilities and configuration options to effectively monitor network activity.
Steps to Access Browsing History on Your WiFi Router
Step 1: Find Your Router’s IP Address
The first step involves locating your router’s IP address, crucial for accessing its administrative interface. Most routers have this information displayed on a label underneath or on the back of the device. Alternatively, Windows users can press the Windows key, type “cmd” into the search bar, and select Command Prompt. Within the prompt, type "ipconfig" and press Enter, noting the number listed as the “Default Gateway.” Mac users should navigate to System Preferences, click Network, select the connected WiFi network, and look for the Router IP address. Typically, addresses look like 192.168.1.1 or similar variations. Writing this down clearly ensures you have immediate access when needed. This IP address will direct you to the router's login page, where you can begin accessing and reviewing your router’s browsing history logs.
Step 2: Log into the Router’s Admin Panel
With your router’s IP address identified, the next step involves logging into its administrative interface. Open your preferred internet browser, enter the router’s IP address into the address bar, and press Enter. You should immediately see a login page requiring a username and password. Usually, routers use default credentials such as "admin" for both fields, though this varies by manufacturer. If these defaults don't grant access, consult your router's manual or visit the manufacturer's website for specific login details. Once logged in, it's advisable to immediately change these default credentials to something unique and secure, reducing the likelihood of unauthorized access. Successfully logging in gives you full control over your router’s settings and access to useful network logs that detail browsing activity on connected devices.
Step 3: Navigate to the Logs or History Section
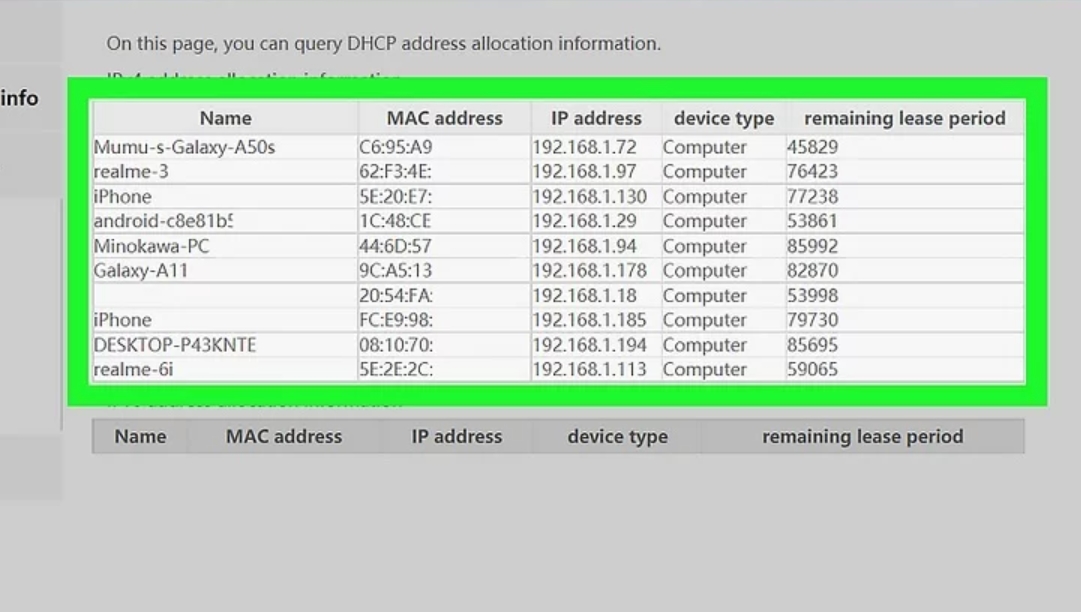
After successfully logging into the admin panel, your next objective is finding the browsing logs or history section. Different routers place this option under varied menus—commonly labeled as "Logs," "History," or "System Logs," or located within advanced settings or security menus. Explore these sections systematically to pinpoint where browsing history data is stored. If your router’s logging feature appears disabled, activate it to start tracking future browsing activities. Keep in mind enabling logging now won't reveal previous browsing history, only data from this point forward. Once located, familiarize yourself with how your router displays logged data, noting devices connected, timestamps, accessed URLs, and IP addresses. Knowing exactly where and how to locate these logs ensures streamlined monitoring of network activity and helps you swiftly identify unusual or unauthorized internet use.
Step 4: Interpret the Logged Data
Effectively interpreting browsing logs requires understanding how data appears within your router’s interface. Router logs typically record visited URLs or IP addresses along with associated timestamps and MAC addresses identifying connected devices. Matching MAC addresses to your known devices (smartphones, tablets, or laptops) helps you quickly identify who accessed specific websites. While URLs clearly show visited sites, logged IP addresses might require additional online tools to reveal corresponding websites. Regular monitoring allows easy detection of unusual or suspicious browsing activity, providing peace of mind regarding network usage. If the data appears overwhelming initially, consider documenting commonly accessed websites for reference. Familiarizing yourself with the typical pattern of your network’s browsing habits helps efficiently detect abnormal activities or unauthorized access, enabling prompt responses and maintaining overall internet security and privacy.
Alternative Methods to Monitor Network Activity
Using Third-Party Firmware
If your router’s default firmware offers limited browsing history logs, third-party firmware like DD-WRT or OpenWRT might offer enhanced tracking capabilities. First, verify if your router is compatible with third-party firmware by checking dedicated firmware websites. If supported, carefully follow the detailed installation instructions provided to flash your router successfully. Installing such firmware significantly expands logging functionality, providing more comprehensive browsing history logs and deeper network insights. Third-party firmware often includes robust tracking features, detailed traffic analysis, and enhanced security measures unavailable with standard firmware. Though installing alternative firmware involves technical knowledge and some risks, when executed correctly, it provides powerful tools for detailed network monitoring. Ensure regular firmware updates to keep security measures current, and carefully follow manufacturer instructions during the initial installation to ensure a stable and secure configuration.
Employing Network Monitoring Tools
Alternatively, you can use dedicated network monitoring tools to complement or replace router-level browsing history checks. Tools such as Wireshark, GlassWire, and NetSpot offer detailed insights into network traffic patterns. Wireshark provides in-depth packet-level data analysis suitable for advanced users requiring comprehensive network visibility. GlassWire offers a user-friendly interface ideal for monitoring real-time network activity, enabling easy tracking of connected devices and visited websites. NetSpot is particularly useful for WiFi performance analysis, identifying interference, and ensuring optimal network operation. These external monitoring solutions simplify tracking online activities without solely relying on router-based logs. While these tools may involve initial setup effort, their ease of use, detailed reporting capabilities, and wide-ranging compatibility make them valuable resources, enhancing your ability to manage and secure your home network comprehensively.
Conclusion
Knowing how to check browsing history on WiFi router enhances your control over network security, internet usage, and connected devices' behaviors. While routers differ in available logging features, most allow basic browsing history checks through their admin interfaces. Steps involve obtaining your router’s IP, accessing the admin panel, and locating and interpreting log data. If your router lacks robust logging features, consider third-party firmware or dedicated network monitoring tools for enhanced insights. Regular monitoring allows quick identification and resolution of security threats or unauthorized usage, fostering a safer home network environment. With this guide, you now possess the necessary knowledge to effectively track, interpret, and manage internet activities across your network.
FAQ
Can I see the browsing history of devices connected to my WiFi?
Yes, you typically can, but the detail level depends on your router model and its logging capabilities. More advanced routers record detailed URLs, while basic ones may record minimal data like connected IP addresses and timestamps.
How can I prevent my browsing history from being tracked on a router?
You can prevent router-level tracking by using a VPN (Virtual Private Network). VPNs encrypt your internet traffic, hiding website visits and making browsing data indecipherable to your router and ISP.
Does using Incognito Mode hide browsing history from the router?
No, using Incognito Mode does not hide browsing history from your router. It only prevents your browser from saving history locally. Router logs or external monitoring tools can still record visited websites.